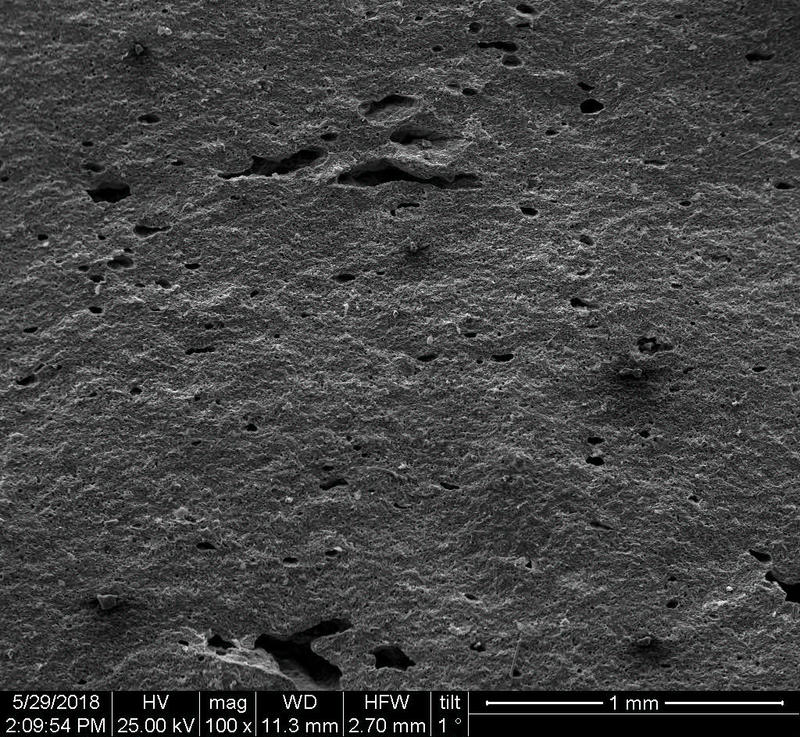
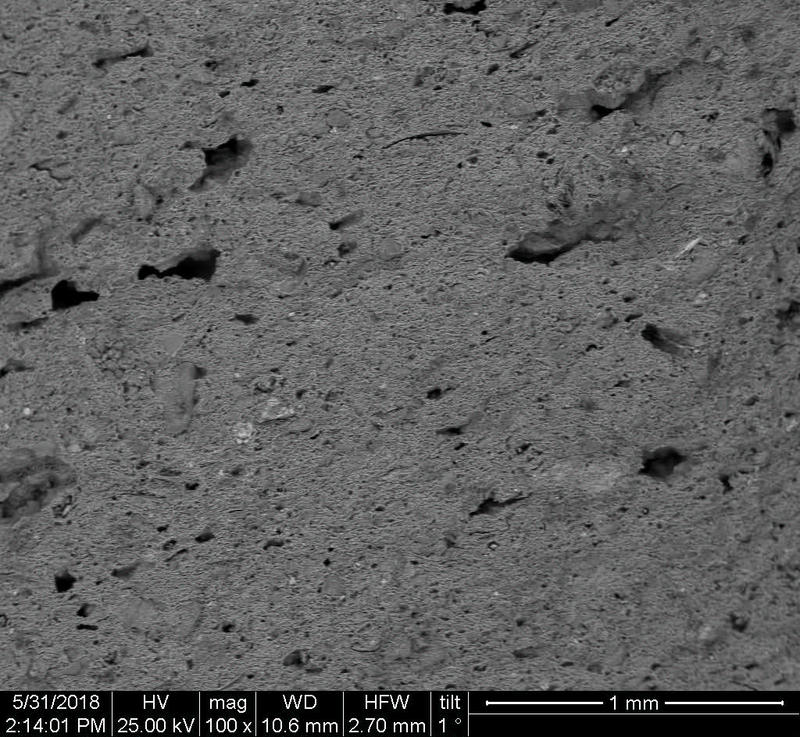
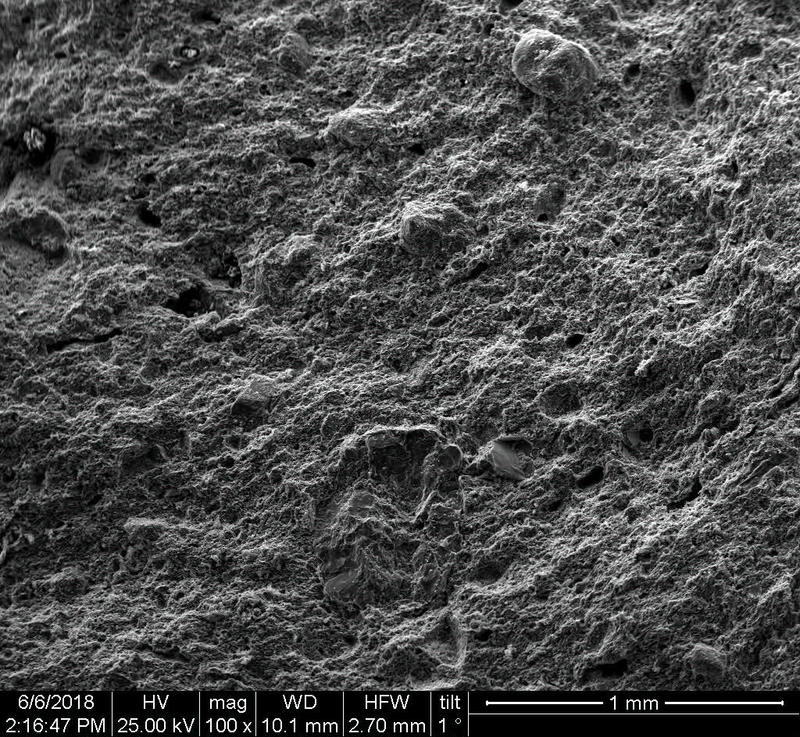
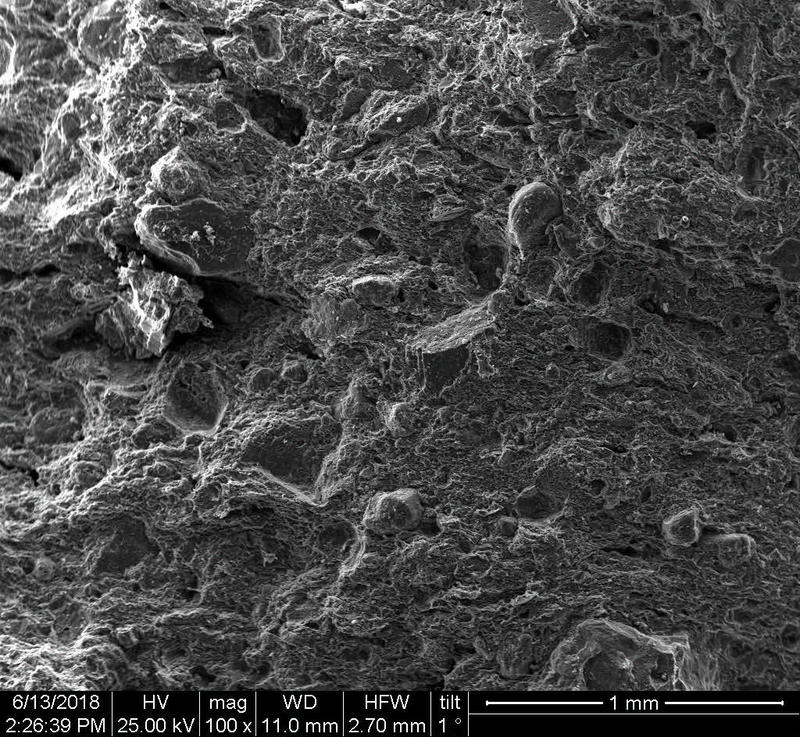
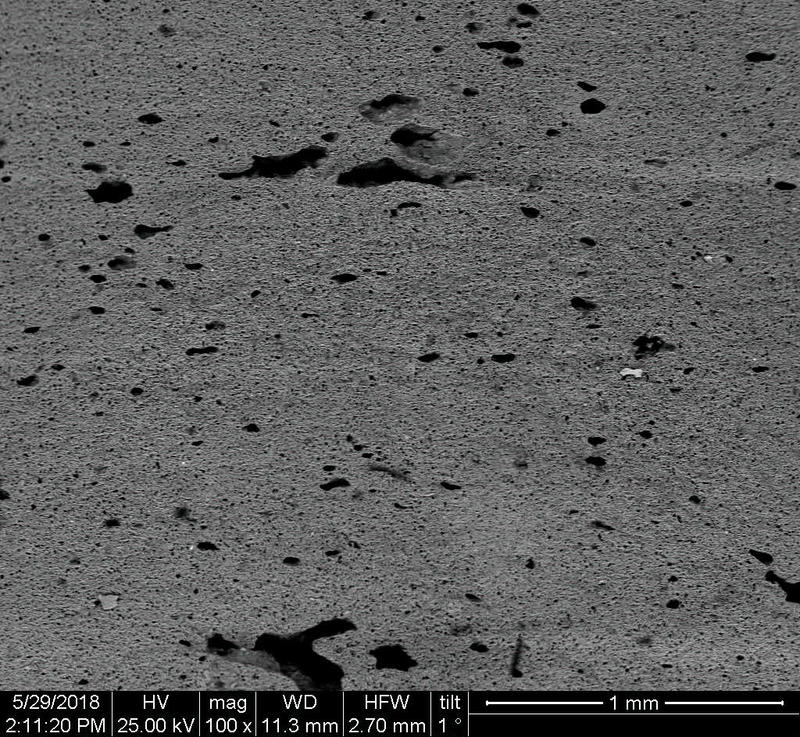
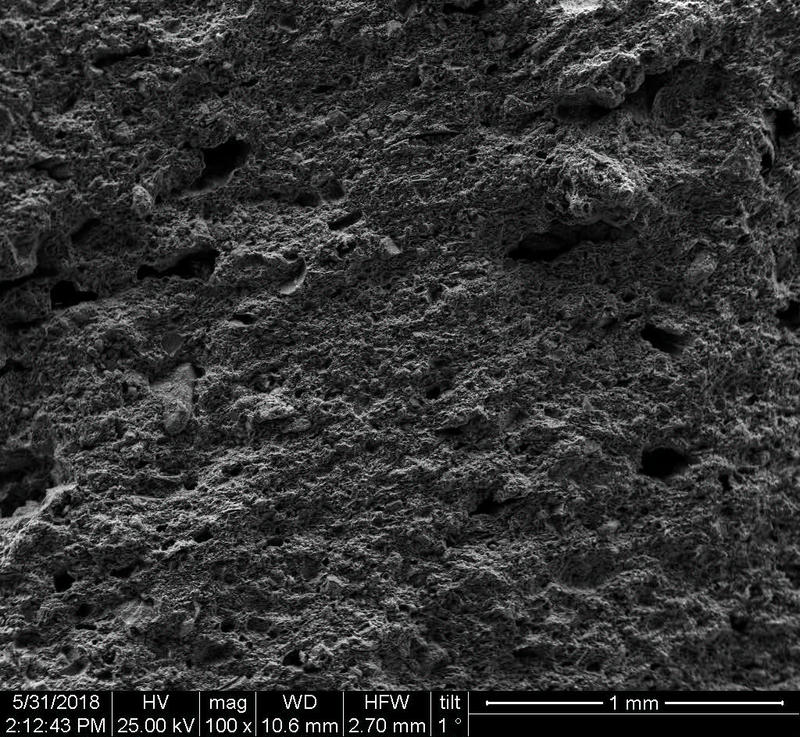
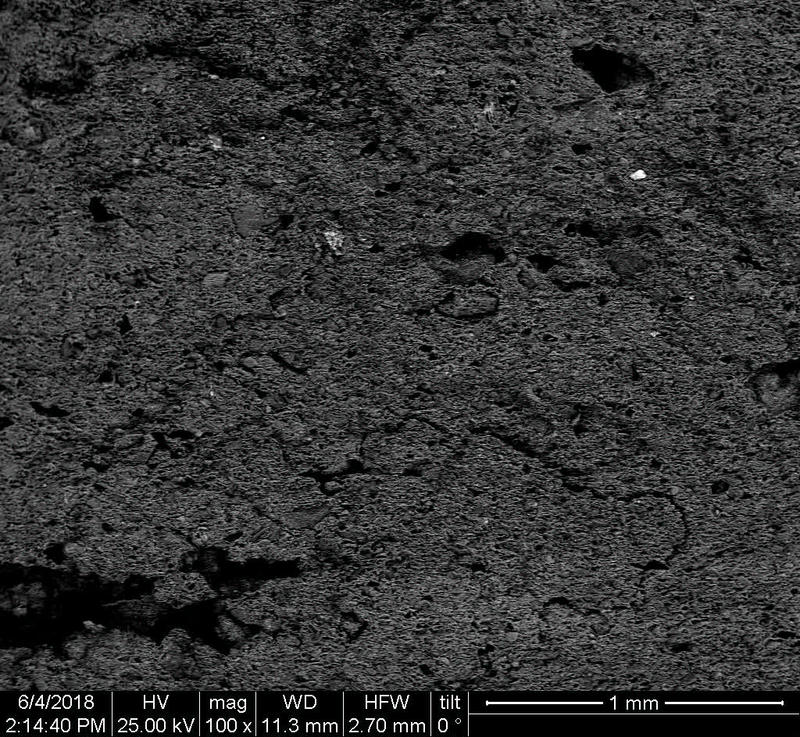
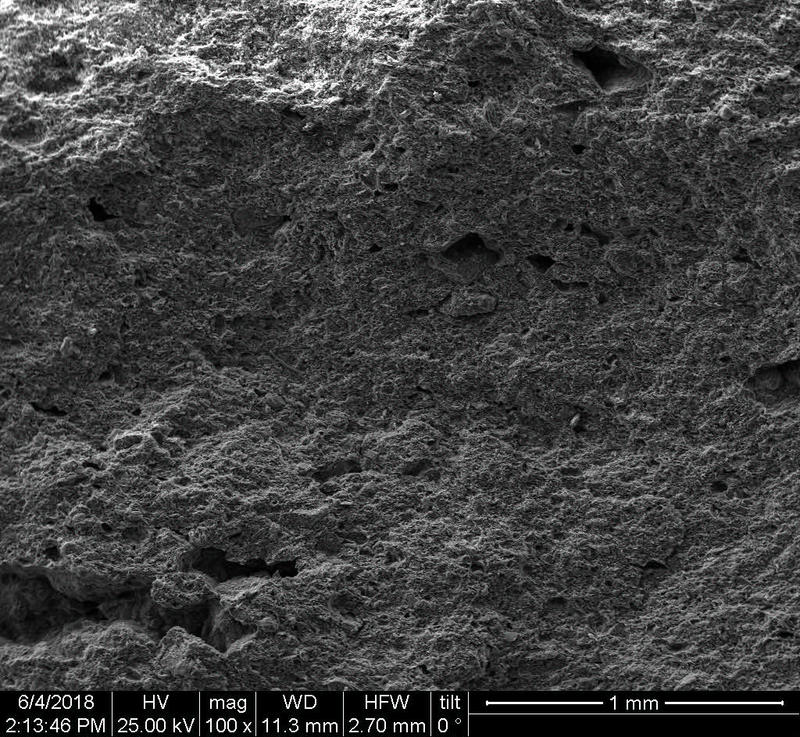
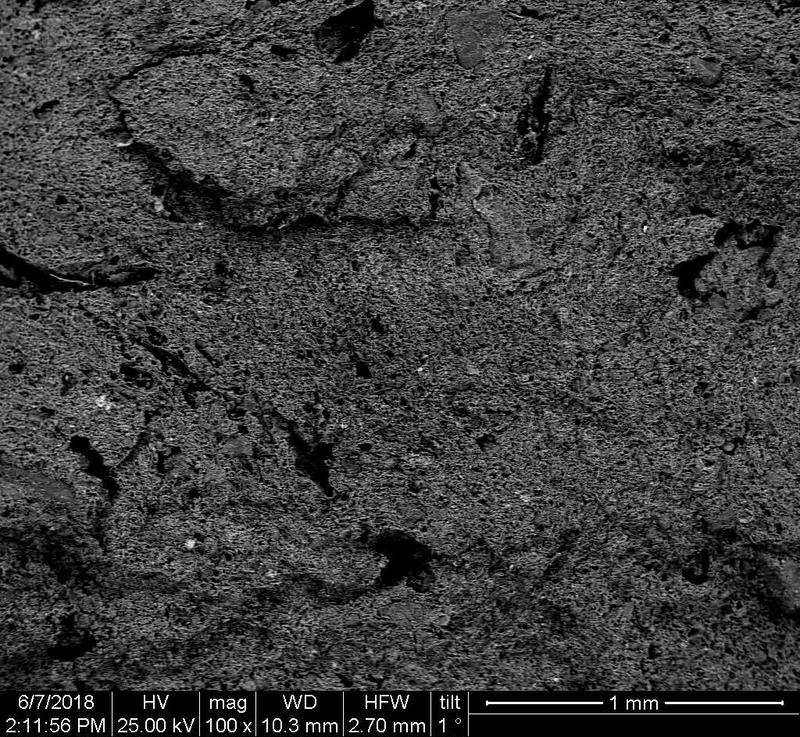
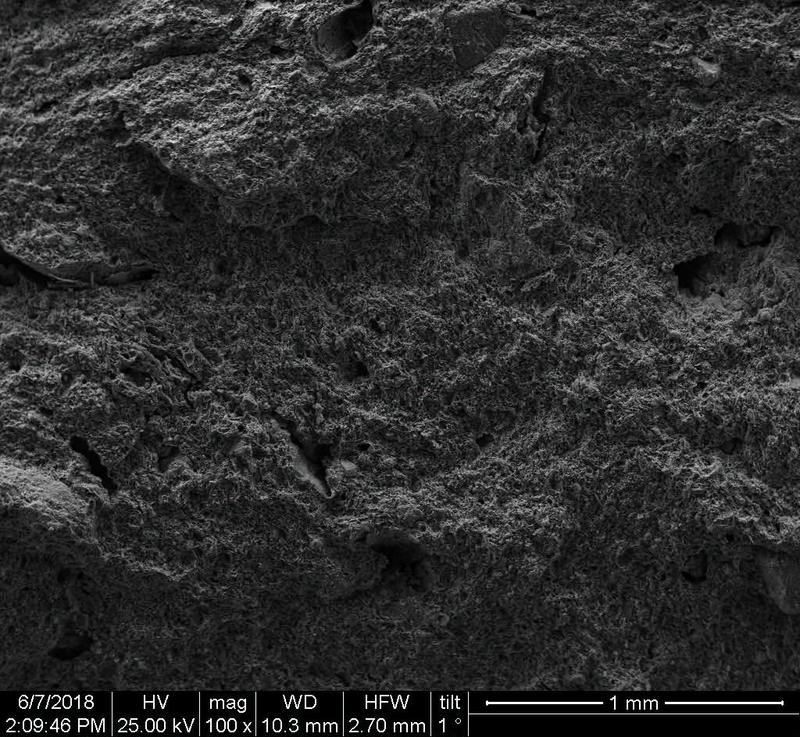
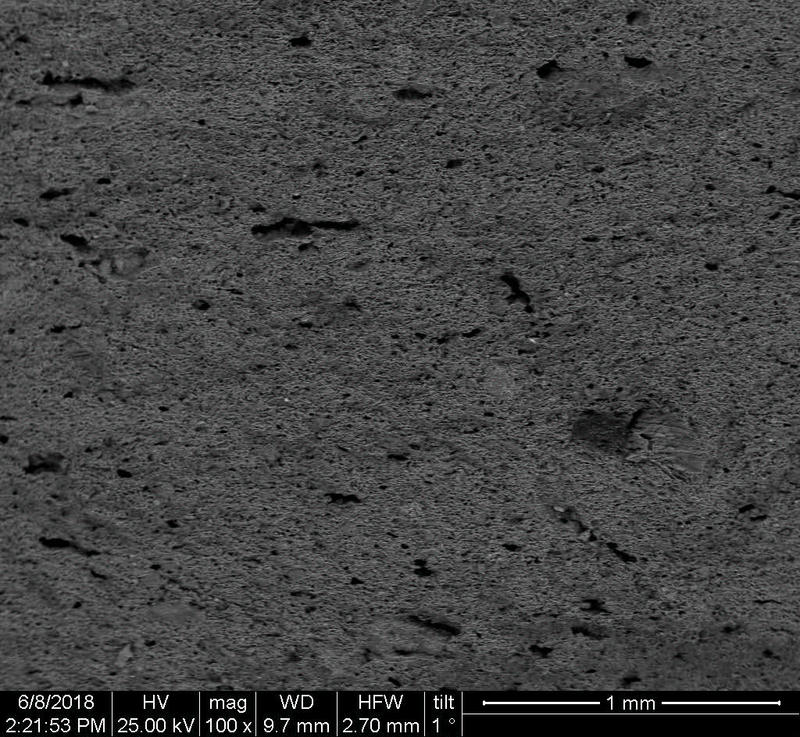
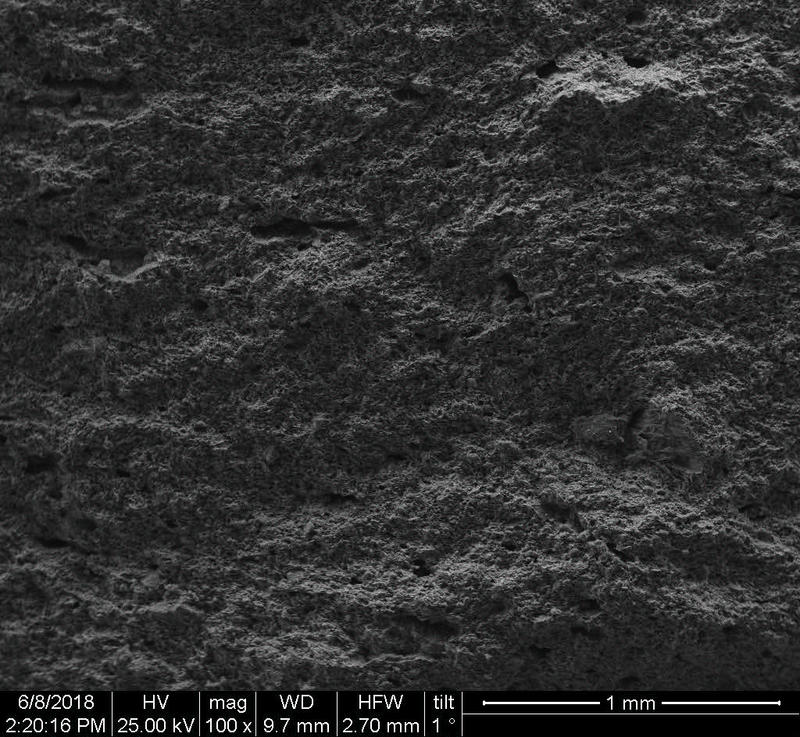
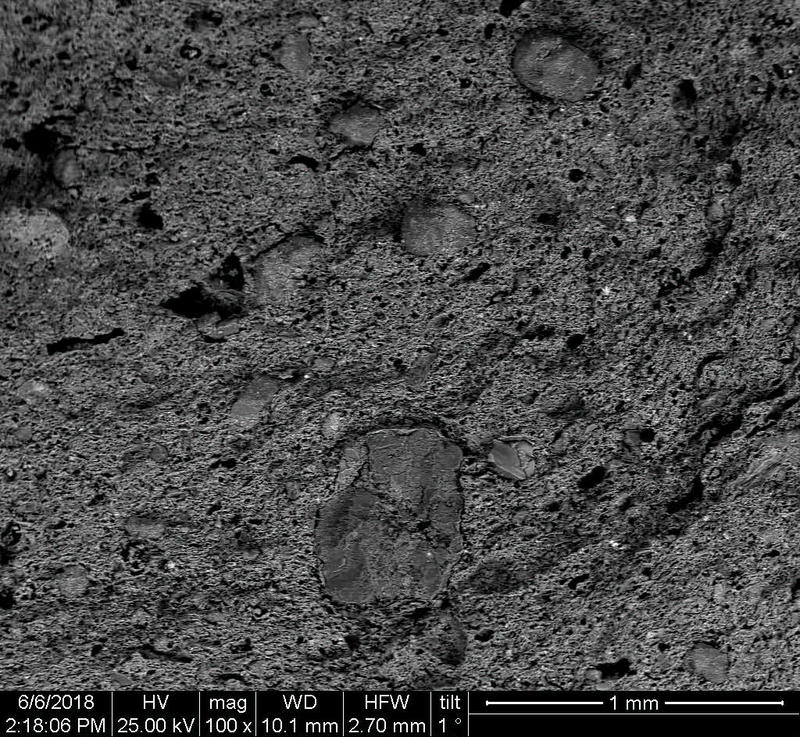
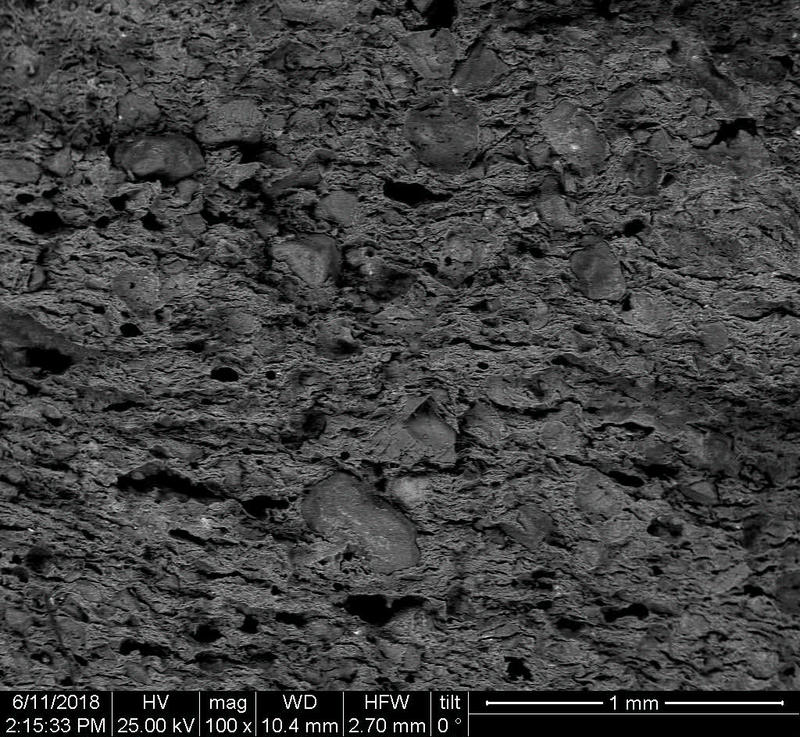
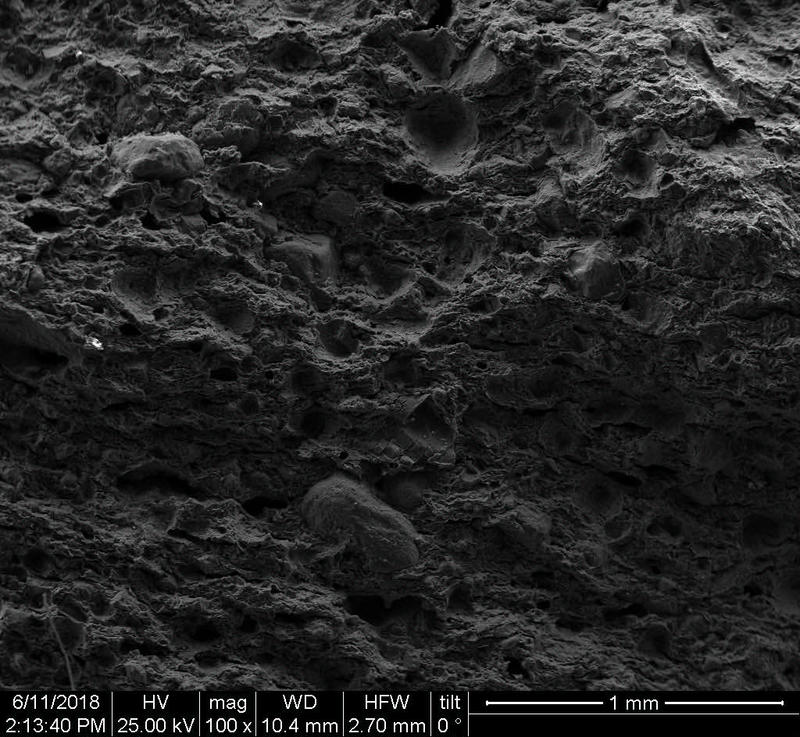
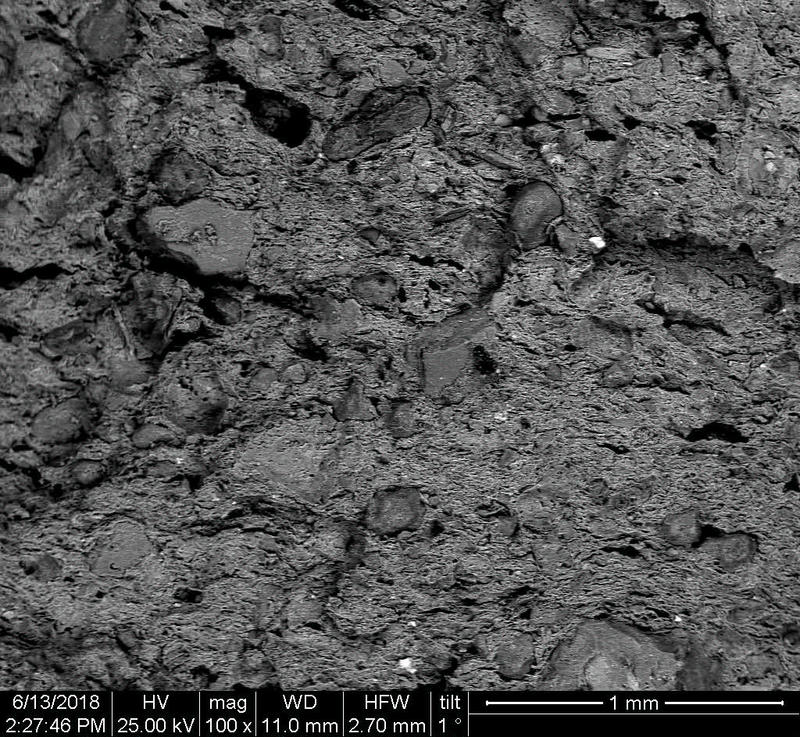
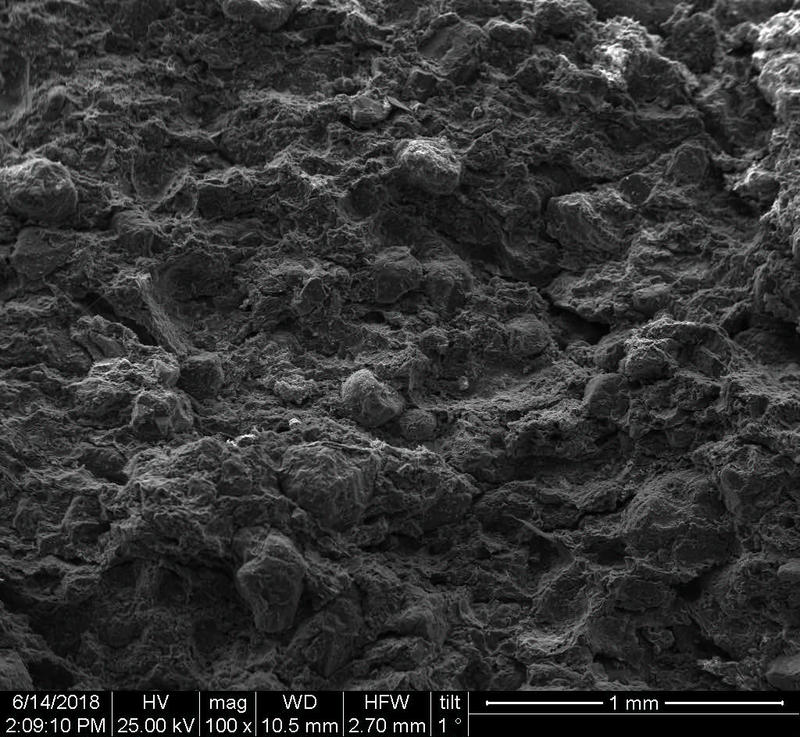
Microstructure
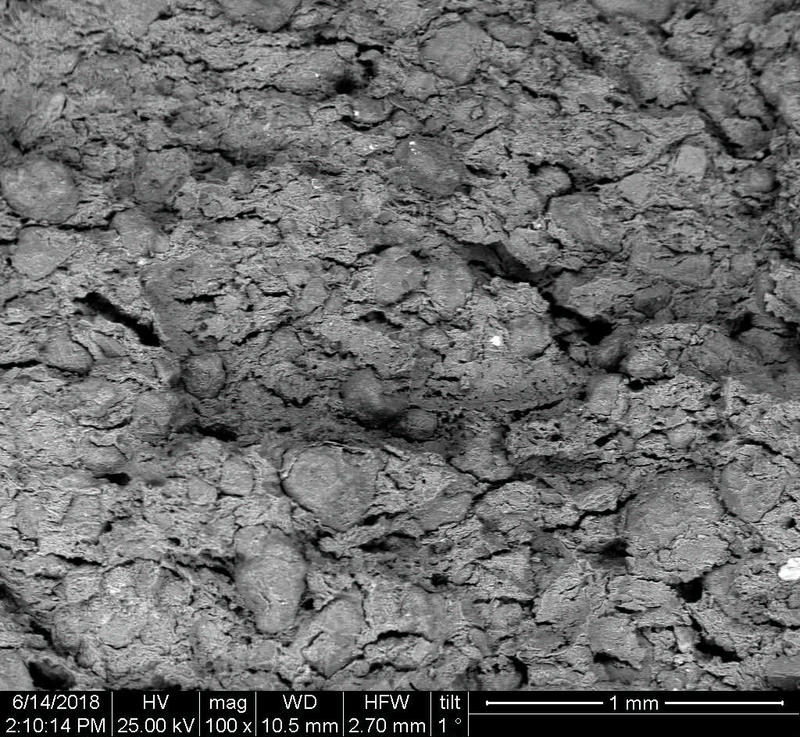
Microstructure of ceramics refers to the composition, identity, shape, and distribution of the different crystalline and glassy phases present in the body matrix.
The study of ceramic microstructure is essential to investigate the raw materials and the preparation techniques used in production. Moreover, microstructural characteristics allow researchers to identify the techniques used in surface decoration and firing.
In addition to the raw material selection and preparation processes, microstructure analyses enable the identification of the physical properties of the raw materials used and the final product produced.
Physical properties of the clay materials such as plasticity and drying shrinkage can be assessed through microstructural images obtained through SEM analyses. Identification of these properties supports the investigation of the physical properties of the potteries produced, such as permeability, thermal shock resistance, and strength.
Archaeological scientists can then interpret the possible reasons behind the potters' choices for particular raw material use and processing.
Questions to think about,
Can you spot the differences? What do you think caused this difference in the microstructure of pottery? Why do you think the backscattered and secondary electron images of the same sample look different?